|
Size: 2624
Comment:
|
← Revision 40 as of 2013-04-10 23:53:00 ⇥
Size: 10998
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 1: | Line 1: |
| {{{#!html <div class="saleshead"> <div class="block" id="left"> <a href="http://4ourth.com/wiki/4ourth%20Mobile%20Touch%20Template"> <div class="salesLeft"> <h3>4ourth Mobile Touch Template</h3> <p>Design for people, not pixels with this handy, wallet-sized inspection and design tool, only $10. <span>Order yours now</span></p> </div> </a> </div> <div class="block" id="right"> <a href="http://4ourth.com/wiki/Mobile%20Design%20Patterns%20Poster"> <div class="salesRight"> <h3>Mobile Interaction Design Patterns Poster</h3> <p>Every pattern from the book and this wiki, plus easy-to-follow relationships, and key information on sizes for readability and touch. <span>Order now</span></p> </div> </a> </div> <div class="salespad"> </div> </div> }}} [[http://www.amazon.com/gp/product/1449394639/ref=as_li_tf_tl?ie=UTF8&tag=4ourthmobile-20&linkCode=as2&camp=217145&creative=399373&creativeASIN=1449394639|{{attachment:wiki-banner-bonus.png|Click here to buy from Amazon.|align="right"}}]] |
|
| Line 2: | Line 28: |
| Status of the hardware and network connections must be available to the user with minimal effort... | You must provide an easily discovered display of the status of important hardware features such as battery level and network connections. The OS provides Annunciator Row features, but you may usually modify or suppress the Annunciator Row within applications. |
| Line 5: | Line 33: |
| {{attachment:AnnunicatorRow-Scroll.png|Figure 1-6. The Annunicator Row is a strip anchored across the top of the viewport. Note that the scroll bar stops at the Annunicator Row, as it does not scroll.|align="right"}} | |
| Line 6: | Line 35: |
| ''Annunciators'' are lights, gauges, or sounds that indicate system status. Annunciator lights and panels date to the dawn of electrical devices. The term was carried over to electronic design, and then to mobile OS design. Though the same feature is often referred to as a “status bar,” this typically implies some overlap with the concept of [[Notifications]], which we will discuss in the next pattern instead. A bar, as shown in Figure 1-6, is displayed along the top of every screen with a series of iconic representations of the status of the device. You should always use common representations and placement of icons, so your users can understand the key indicators on any device without having to learn the specifics of every device. |
|
| Line 9: | Line 43: |
| Always there, almost always visible at all times. Can scroll away, such as by attaching to the top of a window when (e.g. browser) space is needed, but always should be there when new pages are loaded. | The Annunicator Row is present on all screens. It may only disappear or be of lower prominence when other controls disappear as for full-screen game play or video playback. |
| Line 11: | Line 45: |
| And... rarely, sometimes not. Like in camera, but it needs to be available whenever you pull up options, etc. | Certain devices may not require using the space for constant reminders of system status messages. Appliances such as eReaders do not necessarily need an Annunicator Row as their battery life is very long, and network access is needed only intermittently. The status messages will still be needed, and you may be able to solve this with something like [[Notifications]] repurposed to display such information when it becomes critical instead. See that pattern for details on this functionality. |
| Line 13: | Line 47: |
| Emergency notifiers... COULD be done by notifications which see, but could be that when critical things are going on (e.g. low battery) this appears anyway; sub-variant: individual notifiers appear, like a red battery icon, but no others. If the device operates very seamlessly, and has very reliable connectivity (or losses are generally not critical) and long battery life (ePaper devices, and plugged in items like some kiosks or CE devices) then the Annunciator Row may not be needed, and this may be solved with the Notification Area may be repurposed to display such information when it becomes critical instead. |
Kiosks and other devices where the user does not have full control of the device also may not need to display an Annunicator Row to general users. |
| Line 19: | Line 51: |
| Ideally, when space provides, and on touch especially, may provide access to the settings and/or to view more details. | Annunciators are notifiers only. You should generally not allow direct interaction with the items. |
| Line 21: | Line 53: |
| Else nothing. Doesn't do anything, just displays. | For touch and pen devices, it may be desirable to allow the user to select the Annunciator Row as a whole, in order to get more information, or to provide access to settings. You may also accomplish this by combining it with the [[Notifications]] area. |
| Line 25: | Line 57: |
| Bar at the top of the screen. No where else. It's where it's expected... | You should plan to display the default Annunicator Row on every screen. Make a careful, deliberate choice whenever hiding to regain screen real estate or to declutter the screen. Hiding the status icons is generally appropriate for video playback, most games, and many slideshows or similar interfaces. Browsers and readers of ebooks, PDFs, and the like may also benefit from hiding the Annunicator Row once reading or scrolling begins. The Annunicator Row is generally displayed as a row of icons—as in Figure 1-7—laid out on a strip of color, gradient, or other background imagery to separate the icons from other, generally interactive display elements. Scroll bars do not intrude into the Annunicator Row as it does not move, but remains fixed at the top of the viewport. Many devices allow the Annunicator Row to be modified. In general, you should restrict these modifications to display changes, such as switching out the background color, and changing icons to match. You can also use this modification as a half-measure, when completely hiding the status messages might not be the best option. For example, camera applications often use great amounts of battery power, so you could display the battery icon, but no others in order to leave more room for the live preview. If you do this, use the conventional position of the battery icon, simply leaving out all others. {{attachment:AnnunicatorRow-Icons.png|Figure 1-7. Common icons for the vast majority of conditions shown in the Annunicator Row. All items are enabled and at maximum graphical mode. This is an example; some are in conflict with one another, so this would never be seen. From left to right: Mobile network, WiFi, Bluetooth, NFC, Airplane mode, Audio level, Locked, Clock, Network activity and speed, Voicemail waiting, Synch, Location, USB connected, and Battery status.}} Within the row, the status messages are displayed as icons, with as few words or numbers as possible. Use common, universally understood or industry-standard icons whenever available. Icons do not indicate the presence of a feature, but the status of that feature. No display means the icon is not functional, and displaying the icon means it is enabled. Optionally, disabled features may be displayed as grayed-out icons. This can be beneficial to communicate the availability of some features. Use caution to ensure that these are clearly disabled under all lighting conditions. Whenever possible, you can add additional status messages to the icon, such as bars of signal, or of battery level as shown in Figure 1-8. Use simple changes and well-understood signaling such as tall = more and red = bad. {{attachment:AnnunicatorRow-Batteries.png|Figure 1-8. A series of exemplary statuses for the battery, from full to empty, then charging. Using the exclamation point in the icon is clearer than blinking the icon, and is a second code for users or conditions where red is not visible. The power plug icon is clearer to many users than the often-used lightning bolt.|align="right"}} For certain features, whose presence is assumed, you must include explicit measures of their disabling or failure. For example, when no signal is available, the mobile network will have an error “X” in place of the signal bars. |
| Line 29: | Line 77: |
| * Mobile networks. | * Mobile networks |
| Line 31: | Line 79: |
| * Bluetooth * Network Access * * * * Battery * A single item, which changes based on charge level, and state (e.g. being charged) |
* Bluetooth enabled, and activity * NFC or contactless payment enabled * IrDA or other non-wired networking as available * Airplane mode * Input & Output: * Volume, vibrate, or silent modes * Screen or keyboard locks enabled * Network activity * Network speed * Message Waiting Indicator for voicemail, unless this is displayed by the '''[[Notification Area]]''' instead * Synch status or activity * Location services enabled. May or may not indicate when GPS is active * USB cable connected * Power: * Usually a single item, which changes based on charge level, and state (e.g. being charged) * A second battery indicator, as may be displayed on those now-rare devices with outboard (piggyback) or secondary batteries |
| Line 39: | Line 96: |
| The time of day (and sometimes the date) is also present, but may be in any of several places. The most common is centered, followed by right aligned. | The time of day (and sometimes the date) is also present, but may be in any of several places in the row. The most common is centered, followed by right-aligned. Time is always displayed, even on those few devices without an otherwise permanently visible Annunciator Row. |
| Line 41: | Line 98: |
| Naturally, features not included with the device are not given space in the display. Some items may share space, and the highest priority feature or the one with the most important message is displayed. Items are displayed by icon only, whenever possible. Use words only when needed. Refer to my battery blog post about this iconic representation of info... DISPLAY STATUS! NOT JUST THERE, BUT THEY SAY SOMETHING... |
Naturally, features not included with the device are not given space in the display. Some items may share space, and the highest-priority feature or the one with the most important message is displayed. |
| Line 47: | Line 102: |
| Don't let it change all the time. One layout, one size, one type of icon | Don’t let the order or size of the row, or the details of the icons, change with different screens. Use one layout and one type of icon in all situations. |
| Line 49: | Line 104: |
| Except when notifying of special conditions in places where the rest of the bar is suppressed (e.g. battery on a camera screen), do not pick and choose which items to show. Always show the same set in the same manner. | Don’t reinvent the wheel. Reuse existing good design concepts so that users do not have to relearn your icons. How many of those in Figure 1-9 are immediately understandable? {{attachment:AnnunicatorRow-Anti1.png|Figure 1-9. These are just some of the many ways battery charge level is depicted on mobile devices. Many are quite unreadable. Try to pick simple, easy-to-understand symbols, and reuse common icon styles from existing products and best-in-class examples.}} Except when notifying users of special conditions in places where the rest of the bar is suppressed (e.g., battery on a camera screen), do not pick and choose which items to show. Always show the same set in the same manner. Avoid explanations that are jargon-laden. The percentage of usable battery is not nearly as useful as an estimate (even a bad one) of time remaining on a battery. Avoid animations as sole explanations. Mobiles, and especially the status area, are often only glanced at. Blinks will instead be seen as solid on or off at a glance. |
| Line 52: | Line 115: |
| ---- Next: '''[[Notifications]]''' ---- = Discuss & Add = Please do not change content above this line, as it's a perfect match with the printed book. Everything else you want to add goes down here. |
|
| Line 53: | Line 122: |
| Below are a series of annunicator rows (without the rest of the screen) from several devices. You can see the variability, but also how common many elements have become. {{attachment:iPad-1.png|Apple iPad}} {{attachment:hptouchpad.png|HP Touchpad}} {{attachment:Kindle-Fire-(home-1)2.jpg|Amazon Kindle Fire}} {{attachment:Android-GalaxyS-Epic.JPG|Samsung Galaxy-S Epic}} {{attachment:Iphone-iOS5.jpg|Apple iPhone 4}} {{attachment:Android-CasioCommando.JPG|Casio C771 Commando}} {{attachment:Nokia N8-00_008.png|Nokia N8}} {{attachment:Nokia N950_011.png|Nokia N950}} {{attachment:CasioGZONE-Rock.jpg|Casio GzOne Rock}} {{attachment:samsung-sphM320.JPG|Samsung SPH M320}} {{attachment:ClearSpot4Gplus.JPG|ClearSpot 4G Plus}} {{attachment:garminGPS60.JPG|Garmin GPSMap60}} {{attachment:StarTAC.JPG|Motorola StarTAC}} == Make a new section == Just like this. If, for example, you want to argue about the differences between, say, Tidwell's Vertical Stack, and our general concept of the List, then add a section to discuss. If we're successful, we'll get to make a new edition and will take all these discussions into account. |
Problem
You must provide an easily discovered display of the status of important hardware features such as battery level and network connections.
The OS provides Annunciator Row features, but you may usually modify or suppress the Annunciator Row within applications.
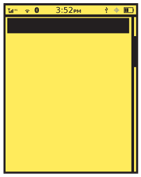
Solution
Annunciators are lights, gauges, or sounds that indicate system status. Annunciator lights and panels date to the dawn of electrical devices.
The term was carried over to electronic design, and then to mobile OS design. Though the same feature is often referred to as a “status bar,” this typically implies some overlap with the concept of Notifications, which we will discuss in the next pattern instead.
A bar, as shown in Figure 1-6, is displayed along the top of every screen with a series of iconic representations of the status of the device. You should always use common representations and placement of icons, so your users can understand the key indicators on any device without having to learn the specifics of every device.
Variations
The Annunicator Row is present on all screens. It may only disappear or be of lower prominence when other controls disappear as for full-screen game play or video playback.
Certain devices may not require using the space for constant reminders of system status messages. Appliances such as eReaders do not necessarily need an Annunicator Row as their battery life is very long, and network access is needed only intermittently. The status messages will still be needed, and you may be able to solve this with something like Notifications repurposed to display such information when it becomes critical instead. See that pattern for details on this functionality.
Kiosks and other devices where the user does not have full control of the device also may not need to display an Annunicator Row to general users.
Interaction Details
Annunciators are notifiers only. You should generally not allow direct interaction with the items.
For touch and pen devices, it may be desirable to allow the user to select the Annunciator Row as a whole, in order to get more information, or to provide access to settings. You may also accomplish this by combining it with the Notifications area.
Presentation Details
You should plan to display the default Annunicator Row on every screen. Make a careful, deliberate choice whenever hiding to regain screen real estate or to declutter the screen. Hiding the status icons is generally appropriate for video playback, most games, and many slideshows or similar interfaces. Browsers and readers of ebooks, PDFs, and the like may also benefit from hiding the Annunicator Row once reading or scrolling begins.
The Annunicator Row is generally displayed as a row of icons—as in Figure 1-7—laid out on a strip of color, gradient, or other background imagery to separate the icons from other, generally interactive display elements. Scroll bars do not intrude into the Annunicator Row as it does not move, but remains fixed at the top of the viewport.
Many devices allow the Annunicator Row to be modified. In general, you should restrict these modifications to display changes, such as switching out the background color, and changing icons to match. You can also use this modification as a half-measure, when completely hiding the status messages might not be the best option. For example, camera applications often use great amounts of battery power, so you could display the battery icon, but no others in order to leave more room for the live preview. If you do this, use the conventional position of the battery icon, simply leaving out all others.
![]()
Within the row, the status messages are displayed as icons, with as few words or numbers as possible. Use common, universally understood or industry-standard icons whenever available.
Icons do not indicate the presence of a feature, but the status of that feature. No display means the icon is not functional, and displaying the icon means it is enabled. Optionally, disabled features may be displayed as grayed-out icons. This can be beneficial to communicate the availability of some features. Use caution to ensure that these are clearly disabled under all lighting conditions.
Whenever possible, you can add additional status messages to the icon, such as bars of signal, or of battery level as shown in Figure 1-8. Use simple changes and well-understood signaling such as tall = more and red = bad.
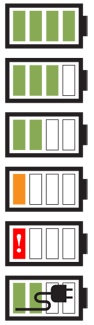
For certain features, whose presence is assumed, you must include explicit measures of their disabling or failure. For example, when no signal is available, the mobile network will have an error “X” in place of the signal bars.
Items are grouped by basic functionality. A conventional order has arisen, from left to right:
- Radios:
- Mobile networks
- Bluetooth enabled, and activity
- NFC or contactless payment enabled
- IrDA or other non-wired networking as available
- Airplane mode
Input & Output:
- Volume, vibrate, or silent modes
- Screen or keyboard locks enabled
- Network activity
- Network speed
Message Waiting Indicator for voicemail, unless this is displayed by the Notification Area instead
- Synch status or activity
- Location services enabled. May or may not indicate when GPS is active
- USB cable connected
- Power:
- Usually a single item, which changes based on charge level, and state (e.g. being charged)
- A second battery indicator, as may be displayed on those now-rare devices with outboard (piggyback) or secondary batteries
The time of day (and sometimes the date) is also present, but may be in any of several places in the row. The most common is centered, followed by right-aligned. Time is always displayed, even on those few devices without an otherwise permanently visible Annunciator Row.
Naturally, features not included with the device are not given space in the display. Some items may share space, and the highest-priority feature or the one with the most important message is displayed.
Antipatterns
Don’t let the order or size of the row, or the details of the icons, change with different screens. Use one layout and one type of icon in all situations.
Don’t reinvent the wheel. Reuse existing good design concepts so that users do not have to relearn your icons. How many of those in Figure 1-9 are immediately understandable?

Except when notifying users of special conditions in places where the rest of the bar is suppressed (e.g., battery on a camera screen), do not pick and choose which items to show. Always show the same set in the same manner.
Avoid explanations that are jargon-laden. The percentage of usable battery is not nearly as useful as an estimate (even a bad one) of time remaining on a battery.
Avoid animations as sole explanations. Mobiles, and especially the status area, are often only glanced at. Blinks will instead be seen as solid on or off at a glance.
Next: Notifications
Discuss & Add
Please do not change content above this line, as it's a perfect match with the printed book. Everything else you want to add goes down here.
Examples
Below are a series of annunicator rows (without the rest of the screen) from several devices. You can see the variability, but also how common many elements have become.







Make a new section
Just like this. If, for example, you want to argue about the differences between, say, Tidwell's Vertical Stack, and our general concept of the List, then add a section to discuss. If we're successful, we'll get to make a new edition and will take all these discussions into account.

